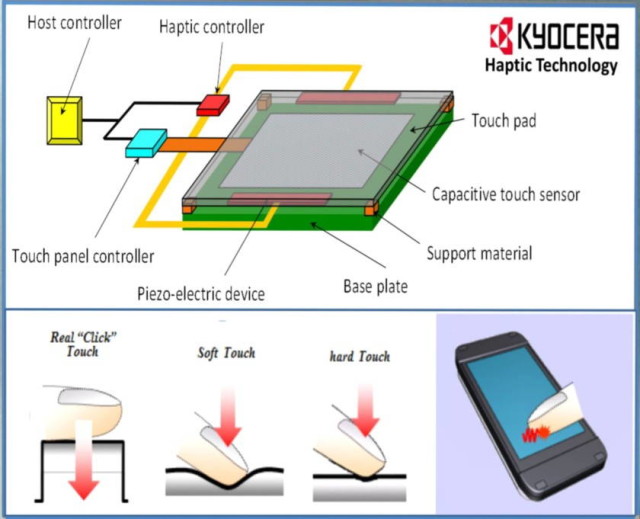
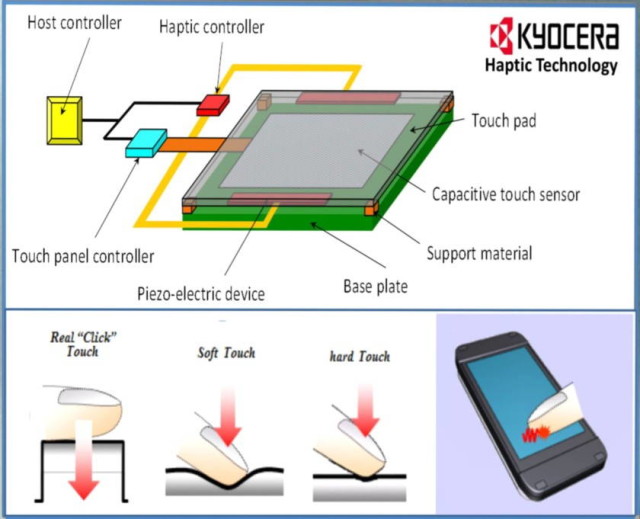
Haptic Feedback Technology: A Deep Dive into the World of Touch
In an increasingly digital world, the sense of touch often takes a backseat. We interact with devices through screens, keyboards, and mice, but rarely do we feel the virtual world. Haptic feedback technology is changing that, bridging the gap between the digital and physical realms by providing users with tactile sensations that correspond to their interactions.
What is Haptic Feedback?
Haptic feedback, also known as haptics or kinesthetic communication, is a technology that uses the sense of touch to provide users with information or feedback. It recreates the sensation of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user. This can range from a simple vibration in a smartphone to a complex simulation of textures and shapes in a virtual reality environment.
The word "haptic" comes from the Greek word "haptikos," meaning "able to come into contact with." Haptic feedback engages our sense of touch to enhance experiences, provide intuitive feedback, and create more immersive interactions with technology.
How Does Haptic Feedback Work?
Haptic feedback systems work by stimulating the tactile receptors in our skin and muscles. These receptors send signals to the brain, which interprets them as different sensations, such as pressure, vibration, texture, and temperature.
There are two main types of haptic feedback:
- Tactile Feedback: This type of feedback provides sensations on the surface of the skin. It can include vibrations, textures, and temperature changes. Tactile feedback is often used in smartphones, gaming controllers, and touchscreens to provide users with confirmation that their actions have been registered.
- Force Feedback: This type of feedback applies forces to the user’s body, creating the sensation of resistance, weight, or movement. Force feedback is commonly used in robotics, medical training, and virtual reality simulations to allow users to interact with virtual objects in a realistic way.
Applications of Haptic Feedback Technology
Haptic feedback technology has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
- Gaming: Haptic feedback enhances the gaming experience by allowing players to feel the impact of explosions, the recoil of weapons, and the texture of different surfaces. Gaming controllers with haptic feedback provide a more immersive and engaging experience, making games more realistic and enjoyable.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Haptic feedback is crucial for creating realistic and immersive VR and AR experiences. By providing tactile sensations that correspond to virtual objects, haptic feedback allows users to interact with virtual environments in a more natural and intuitive way. For example, users can feel the texture of a virtual object, the weight of a virtual tool, or the resistance of a virtual surface.
- Medical Training: Haptic feedback is used in medical simulators to provide realistic training experiences for surgeons and other medical professionals. Surgeons can practice complex procedures on virtual patients, feeling the resistance of tissues, the texture of organs, and the sensation of using surgical instruments. This allows them to develop their skills and gain experience in a safe and controlled environment.
- Robotics: Haptic feedback is used in robotics to allow operators to remotely control robots with greater precision and dexterity. By providing tactile feedback, operators can feel the forces and textures that the robot is interacting with, allowing them to perform delicate tasks with greater accuracy. This is particularly useful in hazardous environments, such as nuclear power plants or disaster zones.
- Automotive Industry: Haptic feedback is used in automotive systems to provide drivers with alerts and warnings. For example, haptic feedback can be used to alert drivers when they are drifting out of their lane, when they are approaching an obstacle, or when they are falling asleep. Haptic feedback can also be used to enhance the driving experience by providing tactile feedback on the steering wheel or pedals.
- Mobile Devices: Haptic feedback is commonly used in smartphones and tablets to provide users with confirmation that their actions have been registered. Vibrations, clicks, and other tactile sensations provide a more intuitive and satisfying user experience. Haptic feedback can also be used to enhance accessibility for users with visual impairments.
- Education: Haptic feedback can be used in educational settings to enhance learning and engagement. For example, students can use haptic devices to explore the textures of different materials, the shapes of geometric figures, or the anatomy of the human body. This can make learning more interactive and memorable.
- Accessibility: Haptic feedback plays a vital role in enhancing accessibility for people with disabilities. It provides an alternative form of communication for individuals with visual impairments, allowing them to navigate devices, read text, and interact with digital content through tactile sensations.
Benefits of Haptic Feedback Technology
Haptic feedback technology offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- Enhanced User Experience: Haptic feedback makes digital interactions more intuitive, engaging, and satisfying.
- Improved Safety: Haptic feedback can provide drivers with alerts and warnings, helping to prevent accidents.
- Increased Productivity: Haptic feedback can allow users to perform tasks more quickly and accurately.
- Enhanced Learning: Haptic feedback can make learning more interactive and memorable.
- Greater Accessibility: Haptic feedback can enhance accessibility for people with disabilities.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many benefits, haptic feedback technology also faces several challenges:
- Cost: Haptic feedback devices can be expensive, which can limit their adoption.
- Complexity: Designing and implementing haptic feedback systems can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Standardization: There is a lack of standardization in haptic feedback technology, which can make it difficult to develop interoperable systems.
- Realism: Creating realistic and convincing haptic sensations can be challenging, particularly for complex textures and forces.
Despite these challenges, haptic feedback technology is rapidly evolving, with new innovations and advancements emerging all the time. Future directions for haptic feedback technology include:
- Miniaturization: Developing smaller and more portable haptic feedback devices.
- Wireless Technology: Creating wireless haptic feedback systems that can be used with mobile devices and virtual reality headsets.
- Advanced Algorithms: Developing more sophisticated algorithms for generating realistic and convincing haptic sensations.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Combining haptic feedback with AI to create intelligent systems that can adapt to the user’s needs and preferences.
- Biometric Integration: Integrating biometric sensors with haptic feedback to create personalized and adaptive experiences.
Conclusion
Haptic feedback technology is transforming the way we interact with the digital world. By providing users with tactile sensations, haptic feedback enhances experiences, provides intuitive feedback, and creates more immersive interactions with technology. From gaming and virtual reality to medical training and robotics, haptic feedback is revolutionizing industries and improving lives. As technology continues to evolve, haptic feedback is poised to play an even greater role in our daily lives, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.